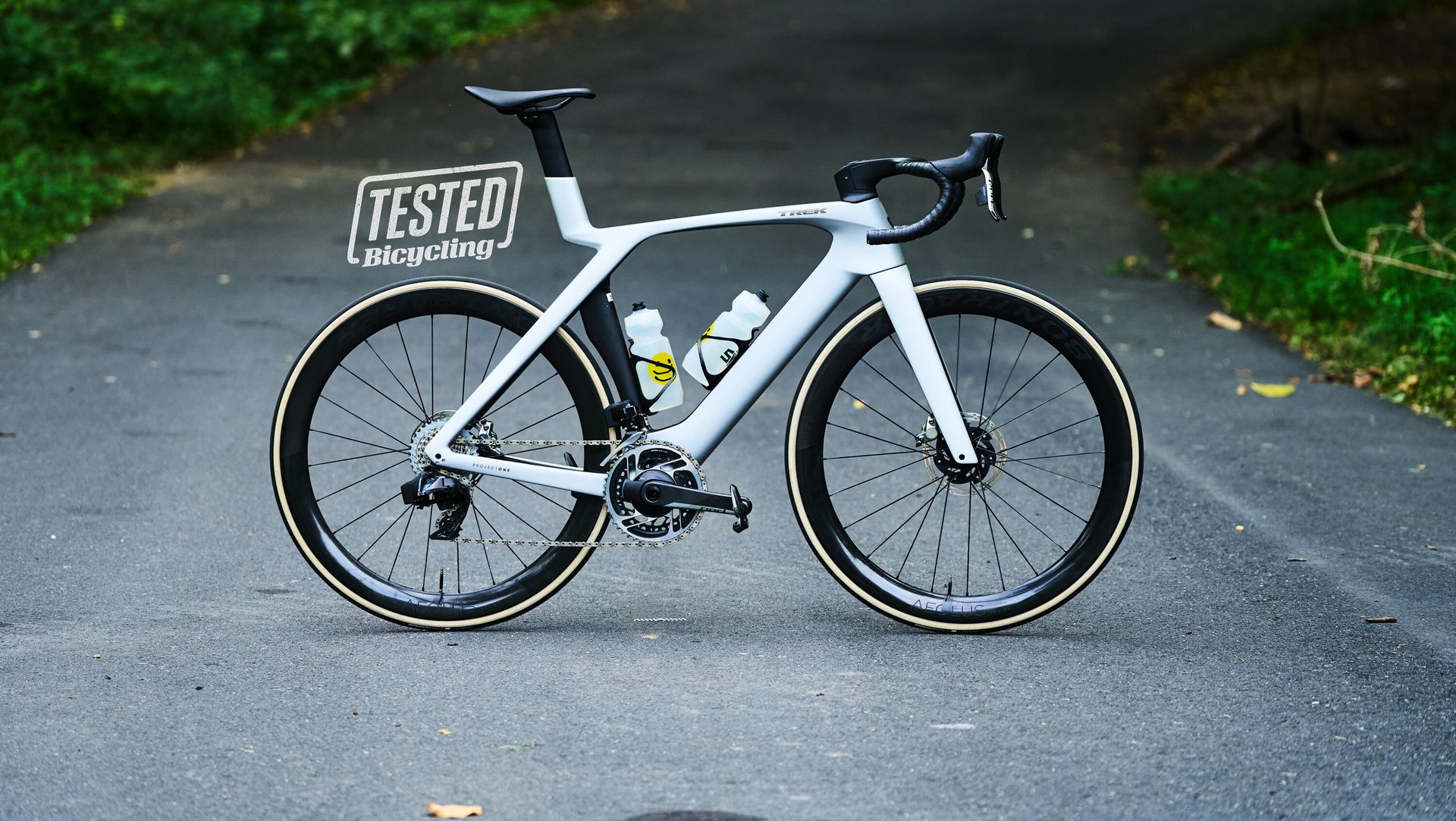
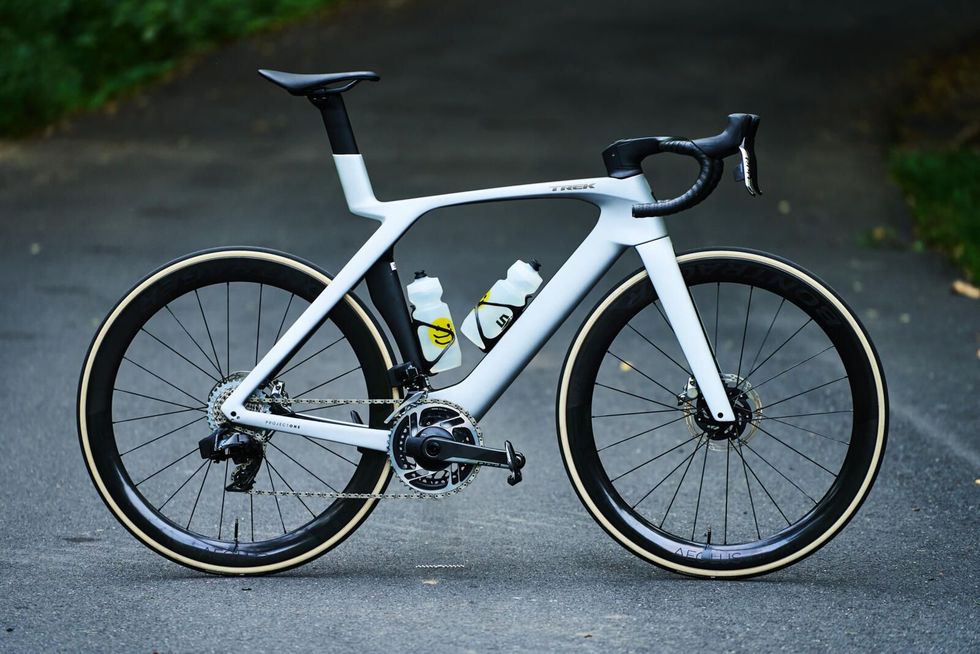
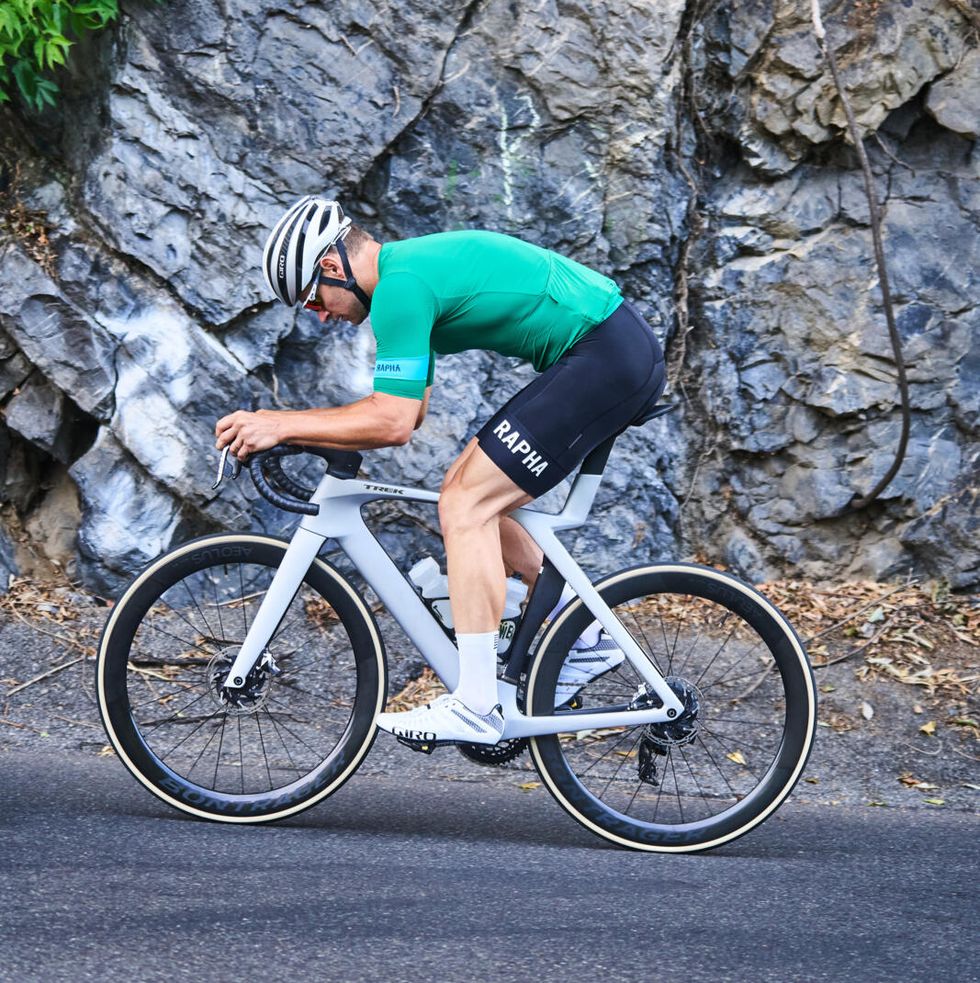
Takeaway: A pure-bred road race bike designed to win at the WorldTour level. With its latest Madone, Trek ditches the IsoSpeed decoupler for the new lighter weight, more aerodynamic, and visually radical IsoFlow seatmast.
- Drops weight and gains efficiency.
- Proven geometry remains unchanged from the gen-6 model.
- Flared bars for reduced drag.
- Three SRAM and three Shimano build kit offerings.
Trek’s Madone is an iconic bike. First launched in 2003, the Madone has evolved massively over the past two decades. The platform’s most significant technological leap came about in 2014 when Trek debuted the Emonda, its dedicated lightweight bike. The Emonda freed the Madone from having to strictly be a light bike, allowing aerodynamics to become its primary focus.
To deal with the notoriously stiff and uncomfortable ride of early aero bikes, Trek’s engineers incorporated an IsoSpeed decoupler, similar to the one used on the brand’s Domane endurance bike. With IsoSpeed, the bike’s seat tube moved independently from the top tube and seat stays, allowing it to absorb road chatter and small bumps. The resulting sixth-generation Madone was incredibly fast against the wind while also receiving praise for its ride quality. But the downside was the added weight.
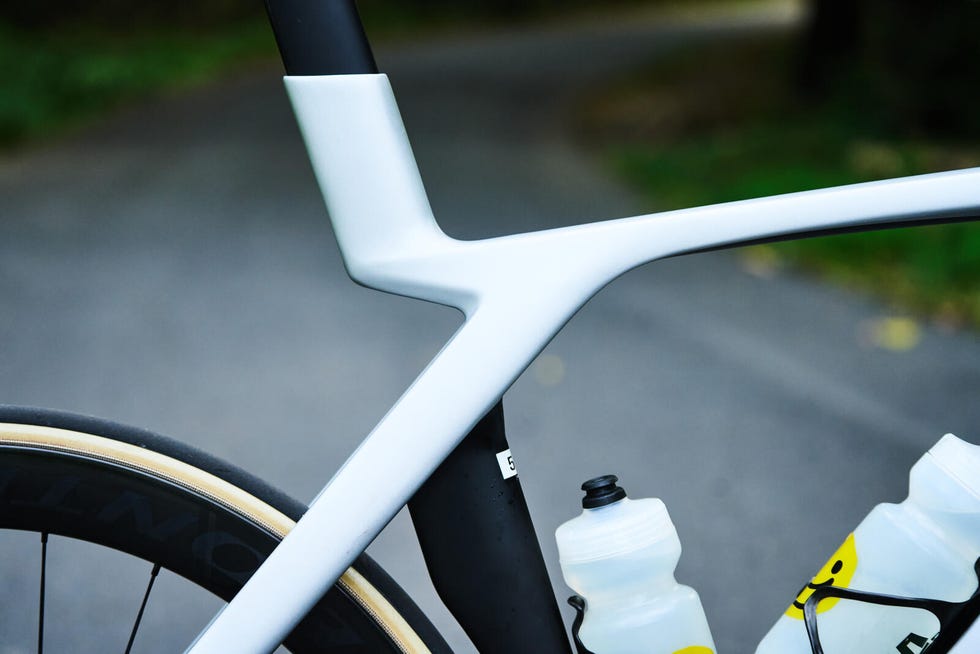
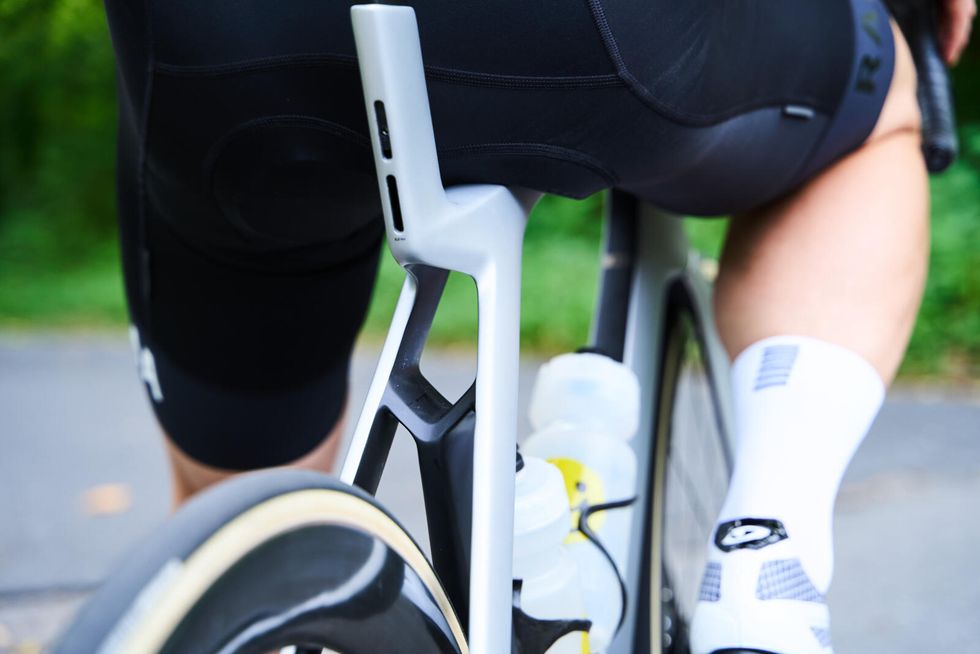
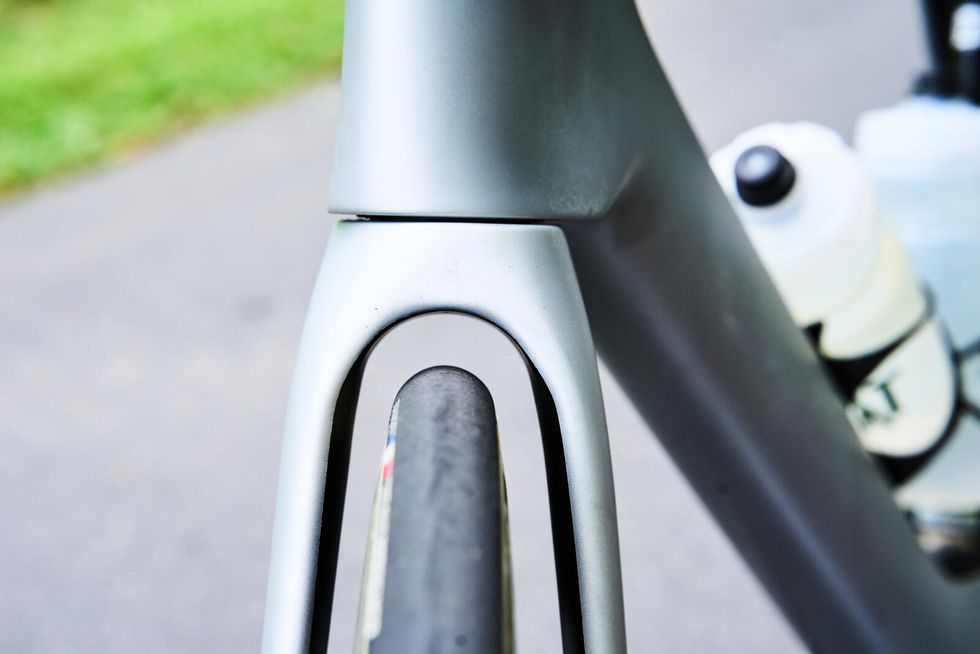
With the new seventh-generation Madone, Trek set an ambitious goal of reducing weight without sacrificing the comfort and aerodynamic properties of the old bike. The most obvious place to shed grams was the IsoSpeed system, now replaced by the visually striking IsoFlow.
According to Trek, function drove IsoFlow’s development. Aided by computational fluid dynamics (CFD), Trek sought to overhaul the entire aerodynamic package of the Madone. The result was a new generation of Trek’s Kammtail tube shapes, including a smoother head tube, a down tube better optimized for use with and without bottles, a taller bottom bracket area, and the radically designed seat tube.
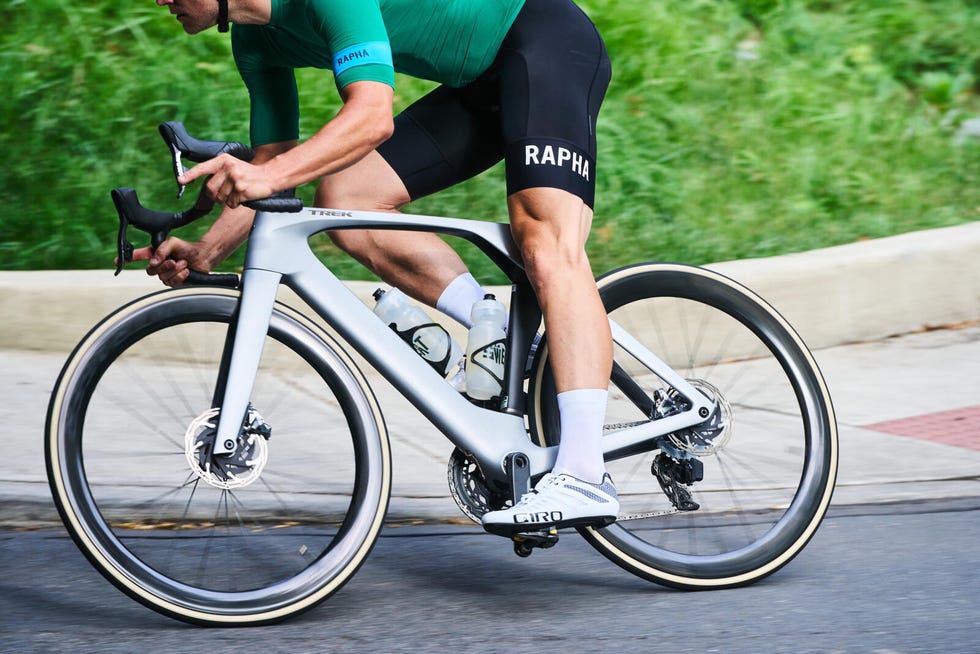
The new Madone is bold and will not be mistaken for any other bike. But it definitely won’t please riders who prefer a more traditional aesthetic. Trek deserves props for pushing the design language of a bicycle forward. Though its looks won't please everyone, I’m happy to see something other than a cookie-cutter, dropped-stays, aero-ish, all-around-er that seems so popular amongst bike designers.
The new seat mast set-up is well-designed, offering easy and consistent height adjustment. But the best detail was in the seat clamp, which allowed for fore and aft adjustment independent of saddle tilt. It’s a small detail that makes setting up the bike much easier, as it allows for minor saddle angle tweaks while leaving it clamped in place.
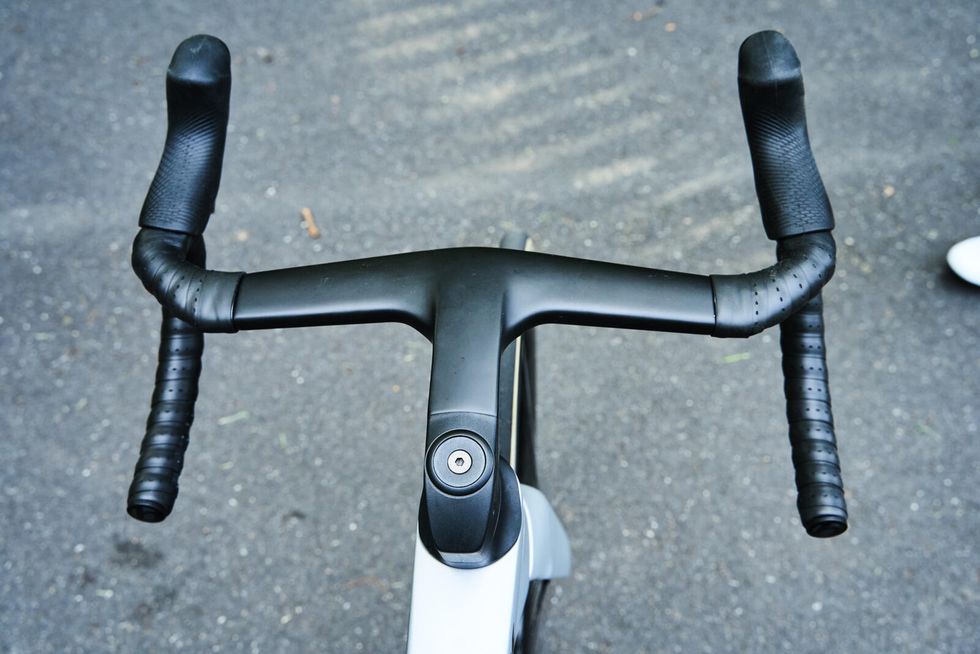
These changes account for roughly half of the aerodynamic improvements of the new bike. Trek claims that the new Madone saves riders 19 watts of pedaling energy at 28 mph, but just half of that savings (9.3 watts) is from improvements to the frame. The remaining watt savings come from changes to the rider position due to the new flared handlebar design. The Madone SLR handlebar measures a traditional width in the drops, but the bar's flare positions the hoods inward by 30mm. This narrower hood location puts the rider in a more aerodynamic position when riding, thus saving watts.
Thankfully for riders that are particular about their contact points, Trek made the new bike compatible with standard 1-⅛” stems so riders can set up their cockpit however they like. However, changing to this would give up a large chunk of the Madone’s claimed aero benefits unless riders choose a narrower-than-normal bar width.
More importantly for pro riders and weight weenies alike, the new frameset is now two-thirds of a pound lighter than its predecessor. Our 56cm test bike came in at 16.2 pounds which is pretty svelt for an aero bike with 51cm deep clincher wheels and disc brakes. A big part of the weight saving comes from the new IsoFlow design. The cantilevered design of the seat tube and IsoFlow allows for engineered flex in the new Madone. This design is how Trek maintains the Madone’s celebrated ride quality.
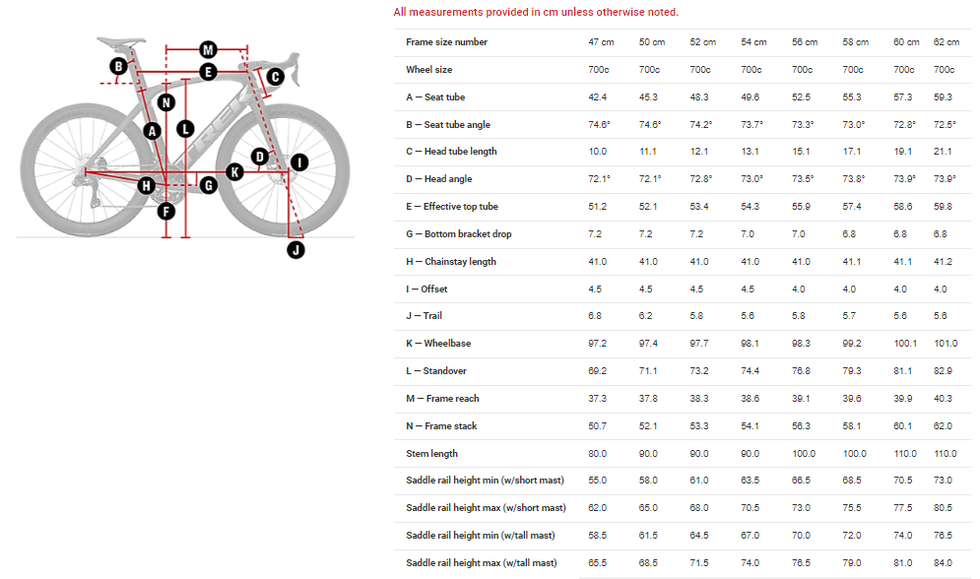
Geometry
Trek stuck to its H1.5 geometry as used on the previous generation Madone. It conceived this as a meeting point between Trek’s old racing-focused H1 geometry and its more relaxed H2 angles. The wheelbase on our 56cm bike was only 983mm, nearly a centimeter shorter than the Specialized Tarmac SL7 and Giant’s TCR, and 13 mm shorter than Canyons Ultimate. Combined with a relatively steep 73.5-degree head tube angle and a 58mm trail figure, you get a bike that will dive into corners as hard as you’re willing to push it.
Pricing and Build Options
There is no getting around the fact that as the top-of-the-line road racing bike from Trek, the Madone is not cheap. The move to electronic-only groups on all builds of the Madone does the price no favors as well. While equivalent new models of the Madone only get $200 more expensive for 2023. The entry-level build for the 2023 Madone SLR 6 (with Shimano 105 Di2) comes in at $8,000. That is a $1,100 increase over the 2021 Madone SLR 6 equipped with mechanical-shifting Shimano Ultegra. Top-of-the-range Dura-Ace and Red eTap builds retail for $12,750 and $13,200, respectively.
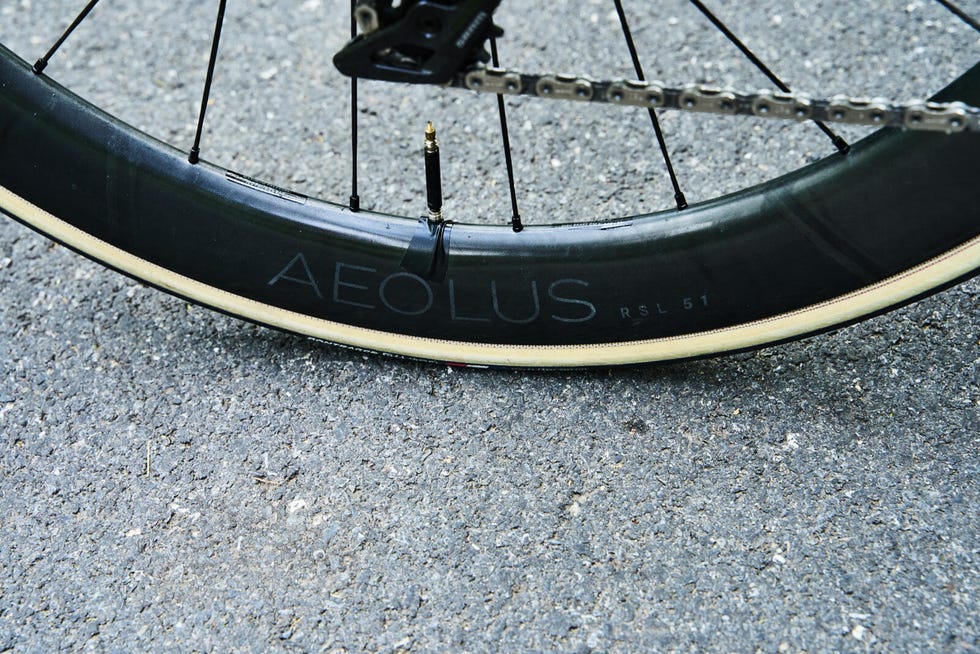
Trek offers the new Madone in six builds, three with SRAM (Red, Force, and Rival eTap) and three with Shimano (Dura-Ace, Ultegra, and 105 Di2). All of the Madone builds ship with the new integrated cockpit; Dura-Ace and Red-equipped Madones ship with Bontrager Aeolus RSL 51 wheels, while all other builds get the slightly heavier Aeolus Pro 51.
Ride Impressions
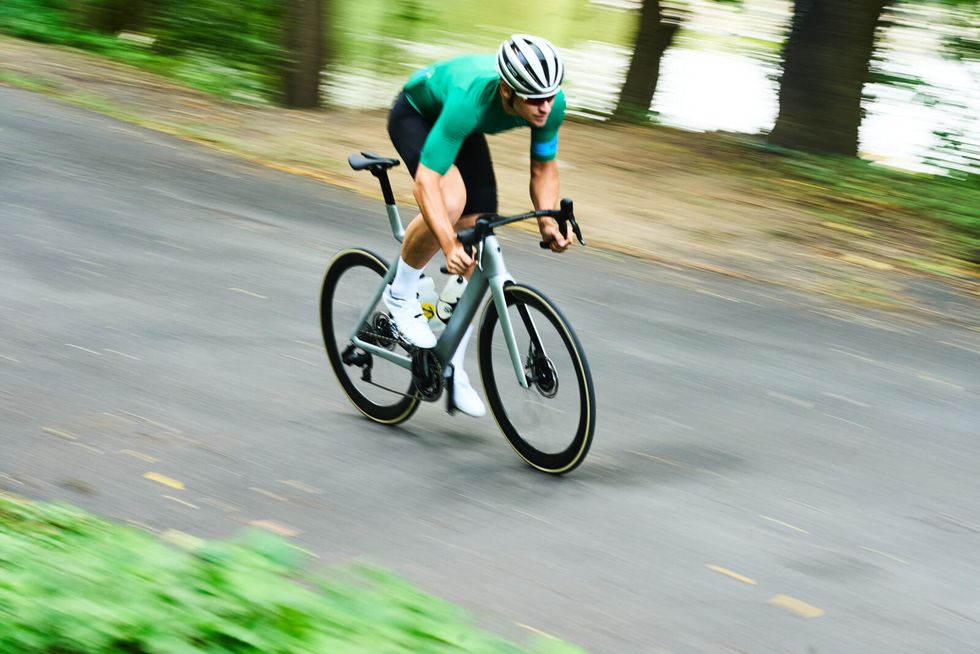
The new Madone has an exceptionally smooth ride, lacking the characteristically dead and harsh feel of past aero bikes. But the mellow ride is not without an edge. The Madone does an exceptional job of balancing all-day comfort with the agility and aggression needed to be a top-tier race bike. Under sharp accelerations, especially at speeds under 25 mph, the Madone felt impressively stiff. But accelerations from the high 20s into 30+mph territory felt a bit more muted, which is not inherently a bad trait. A twitchy bike is not helpful when you’re going that fast.
Once the Madone is up to speed, it just wants to stay there. I was impressed with how quickly and easily the bike would get rolling up to 20-22 miles per hour. Combined with the gentle ride quality, it felt like the new Madone would constantly surprise me with how fast I was going. The sensation of speed on this bike is almost sneaky, you get used to what 25mph feels like on a road bike, but on the Madone, the same pace feels calmer and less frantic, at least in a straight line. Throw the Madone into a corner, and it instantly feels sharp and aggressive.
As a racer, I very much enjoyed the Madone’s willingness to corner aggressively, but it did expose one of the bike's faults. The 25mm tires shipped on our test biker are simply too narrow. Trek claims that the Madone can fit tires up to 28mm, but this feels short-sighted. Wheel brands such as Reserve, Enve, and Zipp now design around a 28mm tire as the default width. There is plenty of space in the frame for wider tires, so Trek is likely very conservative in its stock tire choice and maximum tire width recommendation.
Even riding the stock 25mm tires with pressures as low as 65 psi front and 75 psi rear, the narrow rubber still felt like it was missing grip, with the back end stepping out multiple times when exiting a corner. It was also discouraging that a road bike selling for over thirteen thousand dollars does not ship with tubeless compatible tires or the proper bits to easily set up the Bontrager Aeolus RSL 51 wheels as tubeless.
Another thing missing from the bike was a computer mount. Usually, it is not something I would expect a brand to include, but the bars require a Trek-specific part. Given the complete bike’s price tag and Trek’s integrated cockpit, it should come with a computer mount. I sourced a Blendr mount from my local Trek store, but it was not without its issues (it rattled loose during a training crit and fell off). It is possible to entirely avoid this proprietary part by using a standard 1-⅛” stem and handlebar but making this swap would involve cutting hydraulic houses and would not be cheap.
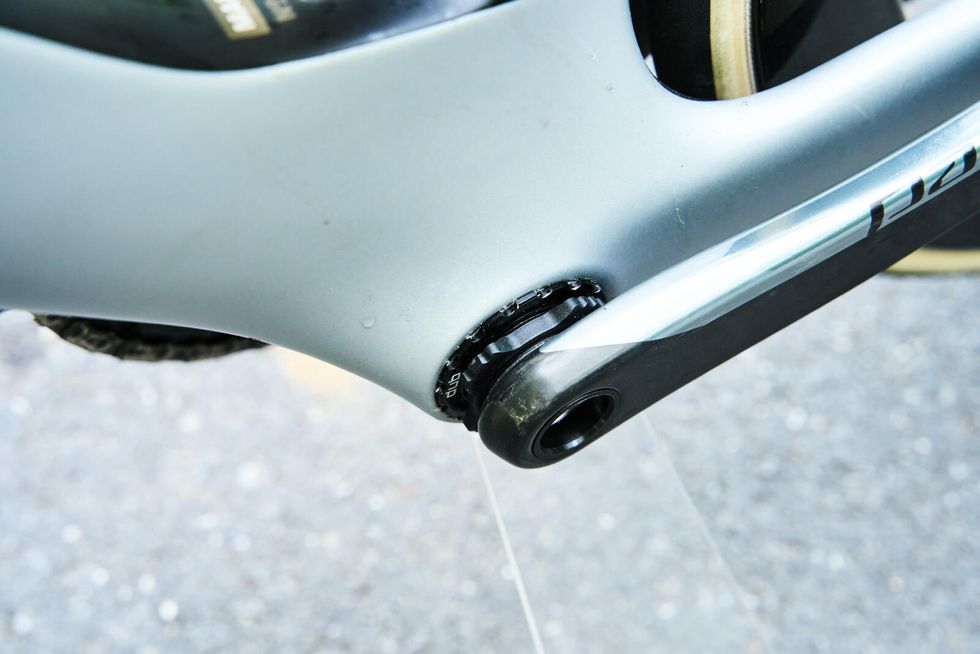
I was also pleased to see Trek continue using the T47 bottom bracket standard on this bike. A threaded bottom bracket shell is a win for mechanics everywhere. However, the latest Madone is now only compatible with electronic shifting. We can argue whether it's bike brands like Trek (releasing electronic-only high-end bikes) or component brands like SRAM and Shimano (no longer developing high-performance mechanical road groupsets) or if consumers are just voting with their dollars. But the result is that we are witnessing the death of mechanical shifting from high-end racing bikes. And that's a little bit sad.
Ultimately this Madone, like the versions that have come before, was conceived and designed to meet the needs of World Tour professionals. Everything about the bike, from how it rides, to how much it costs, reflects that niche design requirement. Aside from a small pool of professional racers, very few people will likely make the most of this bike’s capabilities. It’s analogous to the way most drivers will not benefit from driving a Formula One car. It’s a pure-bred race bike designed to win at the highest level. If that’s what you’re looking to do—or you just want to own a bike with that ability—then the Madone should be on your shortlist.
Test Editor Dan Chabanov got his start in cycling as a New York City bike messenger but quickly found his way into road and cyclocross racing, competing in professional cyclocross races from 2009 to 2019 and winning a Master’s National Championship title in 2018. Prior to joining Bicycling in 2021, Dan worked as part of the race organization for the Red Hook Crit, as a coach with EnduranceWERX, as well as a freelance writer and photographer.