Changing a bike tire after getting a flat is a relatively easy fix—as long as you know how to handle it. Whether you ride on smooth pavement, rough gravel, or rocky singletrack trails, it’s bound to happen eventually, so you might as well prepare yourself with both the necessary tools and the bike repair knowledge you need address the problem.
Below, we detail everything you need to know about how to change a bike tire, including the bike tire repair tips you need to succeed.
First things first though—for tools, you should always carry tire levers, a correctly-sized spare tube, and an inflation device, be it a mini pump or CO2 cartridge. You may also want to consider a patch kit or tire plug, which can come in handy for certain riders. And if you run tubeless tires, scroll down to skip to the tubeless section. When you’re ready to go, here’s your step-by-step guide.
[WATCH] Fix a Flat Tire in 2 Minutes
Follow These Steps to Change a Tire and Fix a Flat
Step 1: Remove the Tire
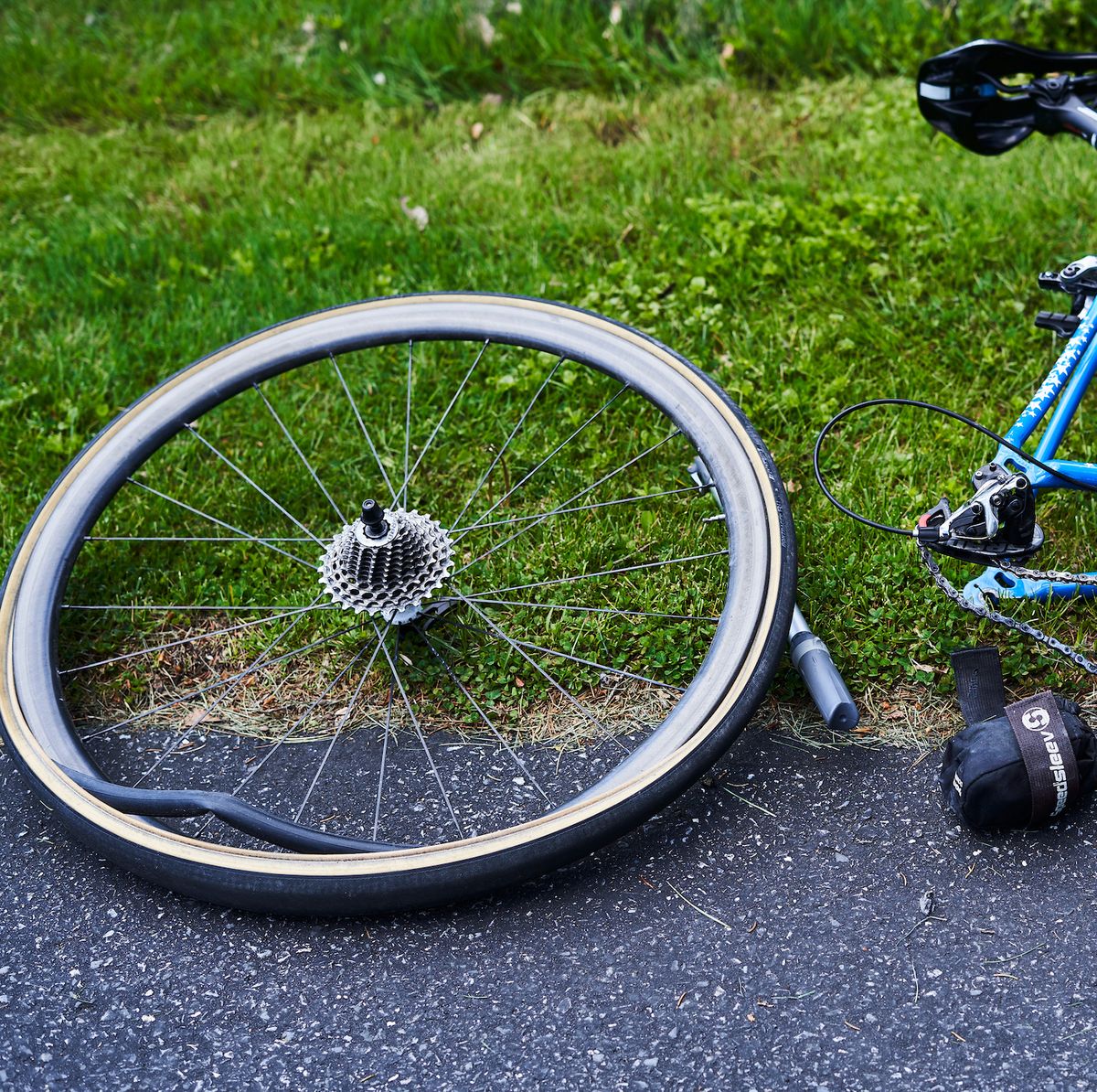
Start by removing the wheel. Keep your bike upright, and if it’s a rear-wheel flat, shift your drivetrain into the hardest gear. If your bike has rim brakes, which many bikes still do, you may also need to loosen the brake.
Next, position yourself on the non-drive side of your bike (opposite the chain) and either open the quick release or unthread the thru-axle to remove the wheel.
Now you can remove the tire. Hook the rounded end of one tire lever under the bead (the outer edge) of the tire to unseat it. Fix the other end to a spoke to hold the lever in place and keep the unseated tire from popping back into the rim. Then hook the second lever under the bead next to the first, pushing it around the rim clockwise until one side of the tire is off. You don’t need to completely remove the tire.
Step 2: Find the Culprit
Once the tire is loose, pull out the old tube (if applicable) and look for the source of the flat, which could be a thorn, piece of glass, or some other sharp object. Carefully run your fingers along the inside of your tire and rim, making sure nothing sharp is left behind; otherwise, you risk getting another flat. Also inspect the outside of the tire, again looking for any foreign object that might still be stuck in the rubber.
If you’re using tubes and want to do a little detective work, pump some air into the old one to find the leak. Two holes side by side indicate a pinch-flat, where the tube gets pinched between the tire and rim. A single hole is a sign that your flat was most likely caused by a sharp object. By lining the tube up with the tire using the valve as a point of reference, you can double check the area where the hole is to ensure the culprit is removed.
Step 3: Patch the Problem
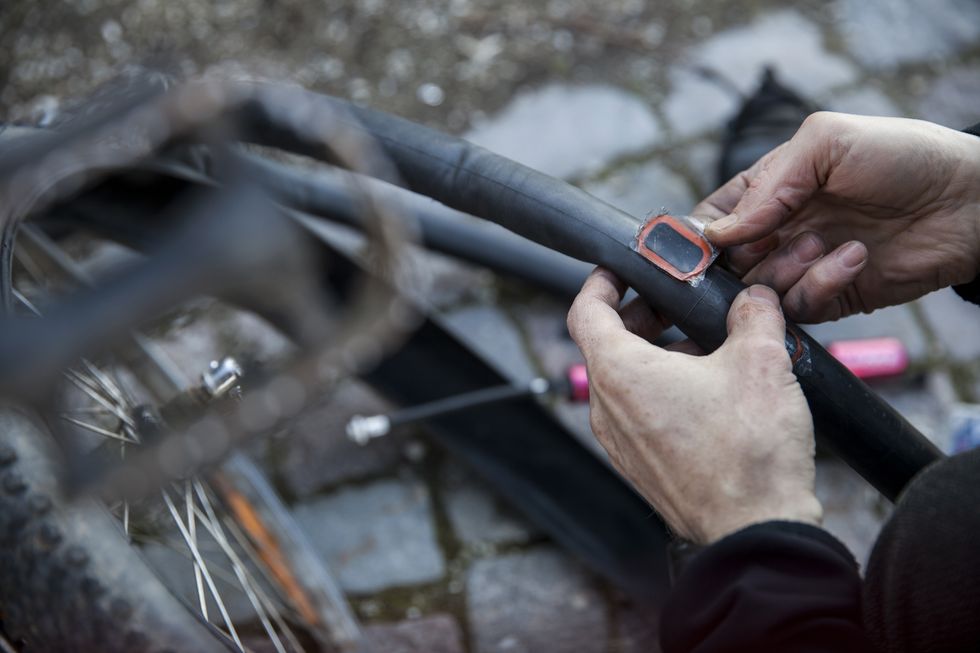
If you’re the thrifty type who likes to reuse old tubes, or if you’ve gotten multiple flats on your ride and have no more spares, then you can patch your tube with a patch kit. If you have a new tube, skip to the next section.
Start by cleaning the punctured area and roughing the surface with an emery cloth. For a glueless patch, simply stick it over the hole and press firmly. For a patch that requires glue, add a thin layer of glue to the tube and patch. Wait for the glue to get tacky, then apply the patch and press firmly until it adheres.
Step 4: Install the Tube
Now inflate your new or patched tube just enough so that it holds its shape. This makes it easier to place inside the tire. Next, with the valve stem installed straight through the rim’s valve hole, position the tube inside the tire. Work the tire back onto the rim with your hands by rolling the bead away from yourself. Try not to use levers to reseat the tire, as you could accidentally puncture your new tube. When you get to the valve stem, tuck both sides of the tire bead low into the rim and push upward on the stem to get the tube inside the tire.
Check to make sure the tire bead isn’t pinching the tube by gently pushing the tire to the side as you work your way around the rim. Then inflate to the appropriate PSI and check that the bead is seated correctly.
Step 5: Reinstall the Wheel
If everything looks good, reattach your wheel, making sure the quick release or thru-axle lever is on the opposite side of your drivetrain.
If you had a rear-wheel flat, lay the top of the chain around the smallest cog on your cassette and carefully push the wheel back into the frame. Close your quick release (and rim brakes if applicable) or insert the thru-axle back into the frame and hub and thread it closed.
Finally, lift the rear wheel and spin your cranks once to make sure everything is back in place and operating smoothly. If all is good to go, get back on your bike and enjoy the rest of your ride.
How to Plug a Tubeless Tire Instead
For tubeless setups—all but standard in mountain biking and becoming increasingly popular on gravel, cyclocross, and even some road bikes—your sealant should do the trick without you even realizing it. Be sure to check your sealant regularly (about every three to six months) to make sure the tire has enough and that it hasn’t dried out.
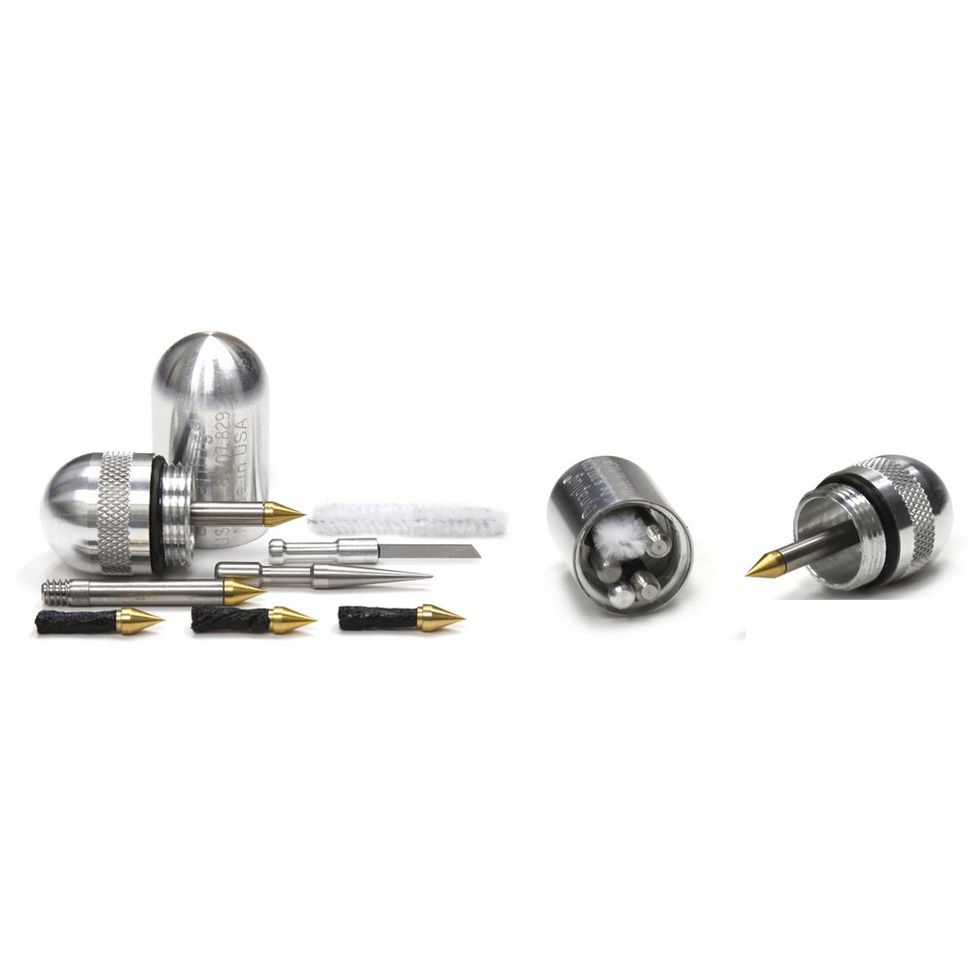
But in the event of a bigger puncture or side-wall tear, you may need a tire plug to stop air loss. Plug kits come with a small strip of rubber and an insertion device, which allow you to plug the hole without even removing the wheel. Once you find the puncture and insert the rubber plug, re-inflate your tire to the appropriate pressure to see that it’s holding air. If so, start riding again, and check the repair every so often to make sure it’s holding fast. You could also add more sealant, but you’d need to carry a valve core removal tool and a small bottle of sealant.
If air loss is coming from a puncture bigger than a plug fix, you could try a patch or a boot on the tire. But fair warning: It’ll likely be difficult to get a patch to adhere to your sealant-coated tire without thoroughly cleaning the area. Adding more sealant or a patch could create another problem, too, by letting all the air out and breaking the seal between the rim and tire. It’ll likely be difficult to reseat the tire bead onto the rim on the spot. The easiest way to ensure your tire holds air at this point is to simply use a spare emergency tube to get through the ride and address it at home or at a bike shop.
When she’s not out riding her mountain bike, Jessica is an editor for Popular Mechanics. She was previously an editor for Bicycling magazine.